78% of the web powered by PHP (3% on PHP 8)
Today, PHP is used by almost 78% of all the websites whose server-side programming language we know. Popular websites such as Slack, Etsy, Wikipedia, WordPress, Mailchimp, Canva, Indeed, Investing.com, and others are powered by PHP.
However, in the coming months, many websites that fail to upgrade to the latest version of PHP 8 will be left running versions that are no longer officially supported. That said, make sure you are at least covered by backporting.
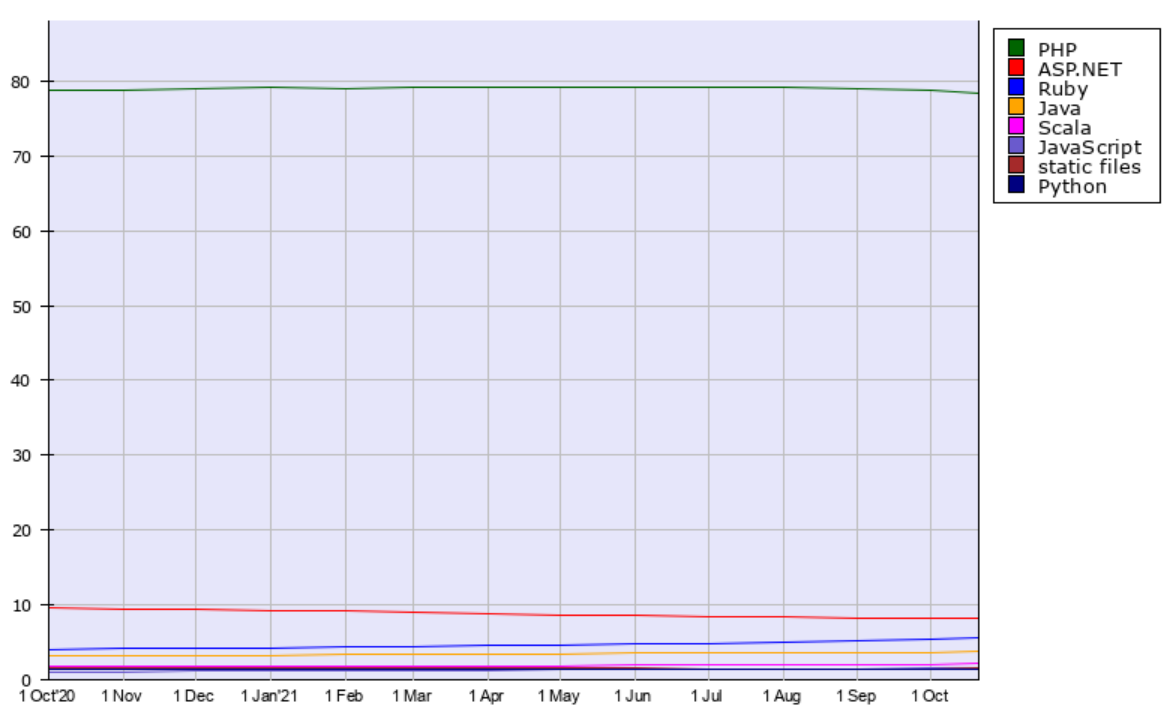
Usage of server-side programming languages for websites (source: w3techs)
PHP 7 EOL (end of life): Upgrade to PHP 8!

PHP 7 was released back in 2015. Meanwhile, PHP 8 was released in November 2020, and as of May 2022, only about 3% of PHP-based websites currently use it!
This slow uptake of PHP 8 will become a much higher priority upgrade for organizations very soon. In fact, PHP 7 loses active support next month and loses security support in six months!
Extended support for PHP 7.4 will end on November 28, 2022. After this date, applications will continue to run; however, those applications will be out of support and at risk of security vulnerabilities that remain unpatched.
In addition, after November 28, 2022, Microsoft will no longer support PHP, and mainly Unix-based distros such as Linux will be the OS supported by future versions of PHP and continued feature, quality, and security updates.
If you would like to upgrade to PHP 8 now, also read this: PHP 8 Compatibility Check and Performance Tips.
Disable expose_php
When enabled, the expose_php parameter communicates to the world that PHP is used on the server. This php.ini setting also exposes which PHP version is installed as reported by the HTTP headers (for e.g., X-Powered-By: PHP/8.0.12). For best security, it is recommended that you disable this php.ini parameter.
Conclusion
Back in 2017, I wrote a similar article. Back then, the majority of PHP-based websites ran an aging PHP version, PHP 5. However, PHP’s extended support had around two years left.
Currently, this is not the case for PHP 7.4; and unless PHP developers announce an extension for their support for PHP 7, there’s sure to be a large chunk of unsupported PHP versions powering the web.
With the recent acceleration of cyberattacks, ransomware, and greater requirements for improved application security and observability, we should all make plans to upgrade to PHP 8 now!
Why does PHP break so much across releases? Part of the problem delaying upgrade is that developers fear breaking their application completely by moving from PHP 7.4 to PHP 8. This has been an issue with PHP from version 4 to current.
Honestly I did not notice that many important breaking changes and the PHP community has tools to detect them. Some of them can even be automatically be fixed.
The real problem is that some important softwares/frameworks did not support PHP 8 until recently:
https://make.wordpress.org/core/handbook/references/php-compatibility-and-wordpress-versions/https://typo3.org/cms/roadmap/https://www.mediawiki.org/wiki/Compatibility/enThe only big exceptions I found are the following:
https://symfony.com/releases/4.4andhttps://github.com/symfony/symfony/issues/41552#issuecomment-919304798https://blog.laravel.com/laravel-php-8-supporthttps://www.drupal.org/docs/system-requirements/php-requirementshttps://downloads.joomla.org/technical-requirementsWelcome to our community! Thanks for the informative post. This indeed is part of the issue.
I’m still blown away by this. 4/5 of the web is powered by PHP?! Wow. I thought everyone hated PHP. Personally I remember liking it, but I haven’t used it in 10+ years. My current website is a Pelican-powered static website written in markdown.
Yes. Of course thats only because we are counting per # of websites on the web. So Facebook counts as 1 site, Youtube counts as 1 website also. On the other hand, if we were counting percentage of daily web traffic, it would most likely be ~ 25% or less I belive. (guessng)