MySQL 8 sample config (my.cnf example) and tuning.
With the release of MySQL 8 I wanted to paste my tuned my.cnf (MySQL configuration file) for discussion, suggestions, and questions. To get the most out of your MySQL 8 installation, you will need to configure it correctly and tune the settings for your specific use case. In this blog post, we will discuss my sample MySQL 8 configuration file and some tips for tuning the settings for optimal performance.
The MySQL configuration file, also known as my.cnf, is a text file that contains configuration settings for your MySQL installation. The file is usually located in the MySQL installation directory, and it can be edited with a text editor.
With the launch of this blog’s Linux forums, I’m hoping that the performance tuning tips that emerge will be from all of us who manage MySQL databases. Recommendations are continued in the comments section at the end of this article.
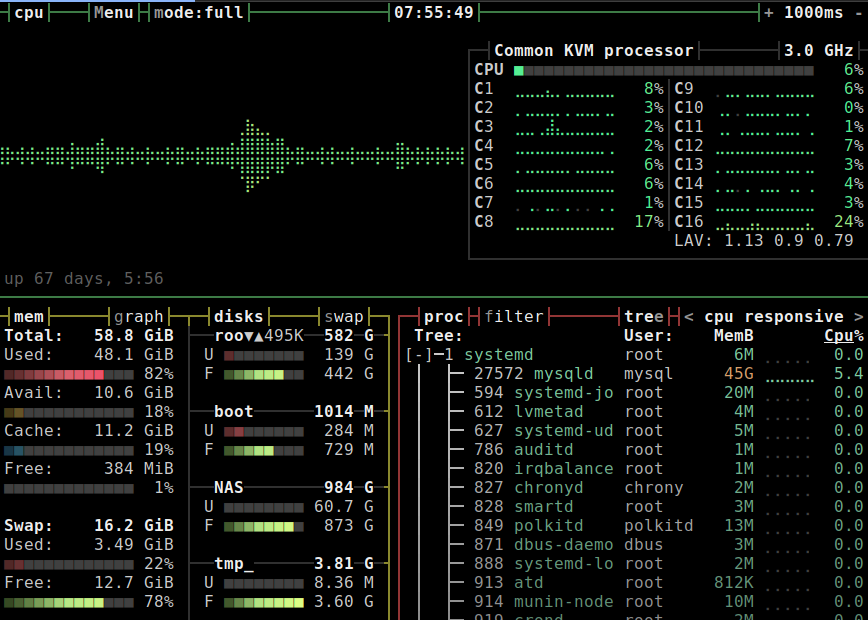
Screenshot from btop showing MySQL 8 memory and CPU usage.
Sample MySQL 8 Config
The my.cnf configuration file shared below is from a standalone MySQL 8 server that was recently separated from a web server. It consistently performs around 9,000 queries per second (QPS) on average.
However, there are occasional spikes where the QPS increases to around 40,000 and lasts for a few days. These events occur roughly 5 to 10 times a year.
Some of the notable config lines are:
max_conections
max_conections is set for the 5 to 10 times per year peak connections,
thread_cache_size
thread_cache_size is set somewhere in between normal traffic and those peak days.
innodb_buffer_pool_instances
innodb_buffer_pool_instances is set to 48 because innodb_dedicated_server automatically sets innodb_buffer_pool_size to 48 GB. See the chart below:
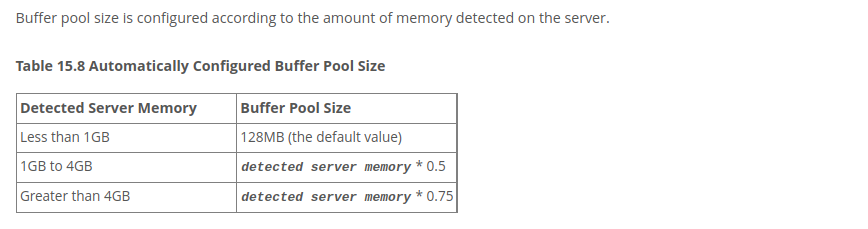
Source: https://dev.mysql.com/doc/refman/8.0/en/innodb-dedicated-server.html
MySQL buffers
For read_buffer_size, join_buffer_size, sort_buffer_size and read_rnd_buffer_size, please read this important tuning article.
Misc.
performance-schema, read Performance Schema Benchmarks: OLTP RW.
disable-log-bin, read How Binary Logs Affect MySQL 8.0 Performance.
Paste of MySQL 8 my.cnf
[mysqld] disable-log-bin = 1 skip-name-resolve = 1 performance-schema = 0 local-infile = 0 mysqlx = 0 bind-address = [IPs removed] open_files_limit = 200000 max_allowed_packet = 256M sql_mode = "STRICT_TRANS_TABLES,ONLY_FULL_GROUP_BY,ERROR_FOR_DIVISION_BY_ZERO,NO_ENGINE_SUBSTITUTION" innodb_dedicated_server = 1 innodb_buffer_pool_instances = 48 innodb_log_buffer_size = 64M innodb_read_io_threads = 12 innodb_write_io_threads = 12 innodb_stats_on_metadata = 0 innodb_file_per_table = 1 max_connections = 500 thread_cache_size = 128 table_definition_cache = 65536 table_open_cache = 65536 wait_timeout = 10 connect_timeout = 5 interactive_timeout = 30 tmp_table_size = 128M max_heap_table_size = 128M read_buffer_size = 256K join_buffer_size = 512K sort_buffer_size = 512K read_rnd_buffer_size = 512K slow-query-log = 1 long_query_time = 2 slow_query_log_file = /var/log/mysql_slow_query.log log-error = /var/log/mysql/db.[removed].com.err
Have questions or suggestions? Add your comment at the end of this article.
MySQL server ‘status’
This is the output of MySQL status for the above MySQL server:
mysql> status -------------- Server version: 8.0.30 MySQL Community Server - GPL Uptime: 37 days 5 hours 39 min 39 sec Threads: 8 Questions: 31068214993 Slow queries: 0 Opens: 36331 Flush tables: 1 Open tables: 36024 Queries per second avg: 9656.974
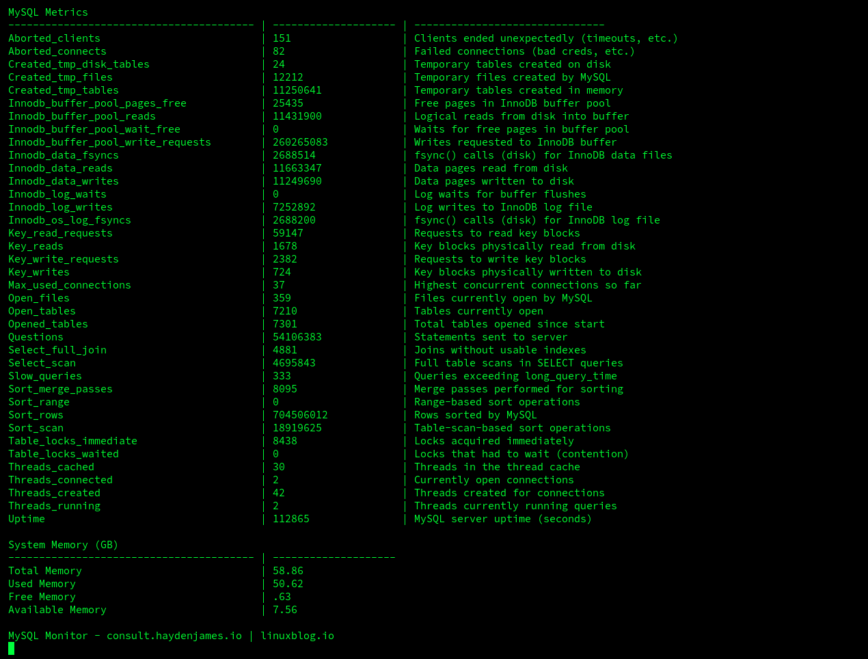
Check out my MySQL Monitor script on GitHub.
Continue reading MySQL performance-related guides
- MySQL Monitor: A Simple MySQL Monitoring Script.
- MySQL Database Performance: Avoid this common mistake.
- Tuning MySQL my.cnf? Avoid this common pitfall!
- MySQL Performance Tuning: Tips, Scripts and Tools.
- MySQL Performance: Stop hoarding. Drop unused MySQL databases.
- Could not increase number of max_open_files to more than… (Solution).
- “MySQL server has gone away” error – Solution(s).
- Linux server performance: Is disk I/O slowing your application?
Published: March 21, 2023 | Updated: January 23rd, 2025
First recommendation is not to depend on
innodb_dedicated_server = 1.When
innodb_dedicated_serveris enabled,InnoDBautomatically configures the following variables:innodb_buffer_pool_sizeinnodb_redo_log_capacityor, before MySQL 8.0.30,innodb_log_file_sizeandinnodb_log_files_in_group.(
innodb_log_file_sizeandinnodb_log_files_in_groupare deprecated in MySQL 8.0.30. These variables are superseded by theinnodb_redo_log_capacityvariable.)innodb_flush_methodOnly enable
innodb_dedicated_serverif the MySQL instance resides on a dedicated server where it can use all available system resources. For example, consider enablinginnodb_dedicated_serverif you run MySQL Server in a Docker container or dedicated VM that only runs MySQL.That said, you won’t gain any performance by using
innodb_dedicated_serverif you instead just set the MySQL variables optimally. So, this setting is more of a convenience, as it will simply automatically configure the variables to ~ what you should be using anyway.Add your tips below.
Suggestion for MySQL 8 enable slow query log and fix those queries. Also choose InnoDB Over MyISAM as MyISAM is old news.
Hello I have a server with mysql 8.034 with RAM 200GB cpu 18 cores i want to tuning my mysql config
I put theses values
############### my tuning ##############
join_buffer_size = 512M
innodb_buffer_pool_size = 160G
innodb_log_file_size = 512M
innodb_log_buffer_size = 512M
interactive_timeout = 200
wait_timeout = 200
skip-name-resolve=ON
do you think that values are correct because i always have full RAM used.
Hi @Baba_Ndiaye
Welcome to our Linux Community
MySQL cannot truly be fined tuned without logging and analyzing at least several hours of runtime stats. (or more for less busy servers)
That said, there are some general mistakes to avoid before tuning.
For example, please read: MySQL Database Performance: Avoid this common mistake
As per the article and MySQL documentation referenced:
your join_buffer is almost certainly too high.
Your wait timeout is far too high. (also see above article)
Also see: MySQL 8 sample config (my.cnf example) and tuning.
If this is a dedicated MySQL server you should use:
innodb_dedicated_serverto avoid misconfig. (as per the above article)Hope this is helpful.