Blockchain & Linux: Exclusive Interview with Hyperledger’s Daniela Barbosa
In this exclusive interview with Daniela Barbosa, Executive Director of the Hyperledger Foundation and General Manager of Blockchain and Identity at The Linux Foundation, we delve into the dynamic and evolving world of blockchain technology. Her leadership in the Hyperledger Foundation illuminates the interplay between blockchain, identity management, and the Linux ecosystem.
Readers will gain a good understanding of how these technologies are shaping the digital landscape and the pivotal role of open-source communities in this transformation.
What is blockchain?
Blockchain is a digital ledger technology that records transactions across a network of computers. It’s known for its security, transparency, and decentralization. This technology is pivotal in various industries for maintaining secure and tamper-proof records. In relation to Linux and the Hyperledger Foundation, blockchain technology is integrated and developed as open-source software, allowing for collaborative, secure, and innovative applications in business and beyond, aligning with the principles of the Linux community.
Learn more – Blockchain: Understanding Its Uses and Implications.
Hyperledger Foundation: Advancing Blockchain in Business & Linux
The Hyperledger Foundation, a part of the Linux Foundation, focuses on building enterprise-grade, open-source blockchain technologies. It provides a collaborative platform for developers and organizations to innovate and develop blockchain solutions that enhance business processes.
With projects like Hyperledger Fabric and Besu, it plays a crucial role in advancing blockchain’s applications in various sectors, ensuring security, transparency, and efficiency. It’s a key driver in integrating blockchain with Linux environments, making these technologies accessible and beneficial to the wider Linux user community.
Get involved – hyperledger.org/participate.
Blockchain & Linux: Q&A with Daniela Barbosa
This insightful Q&A session with Daniela Barbosa, stemming from our interaction at CES 2024, explores the dynamic convergence of blockchain technology with the Linux ecosystem. It offers a deep dive into how these two influential tech spheres are intertwining and evolving together.
-
Could you explain the role of the Linux Foundation in the development and promotion of blockchain technologies?
Answer: The Linux Foundation is a neutral, trusted hub for developers and organizations to code, manage, and scale open technology projects and ecosystems. Linux Foundation’s projects, which include Linux, Cloud Native Computing Foundation (CNCF), Node.js, Hyperledger Foundation, RISC-V, and more, are critical to the world’s infrastructure. Hyperledger Foundation is an umbrella project within the Linux Foundation focused on the open development of enterprise-grade blockchain technologies. We host the world’s largest ecosystem for developing and deploying enterprise blockchain technologies.
-
As Executive Director of the Hyperledger Foundation, what are your primary goals and visions for the foundation?
Answer: Blockchain as a technology is here to stay and our goal for the Hyperledger Foundation is to be the home for the top enterprise blockchain open source projects across many different layer 1 and layer 2s in addition to permissioned DLTs. If you look at the growth of the foundation over the last 8 years with our new projects and communities, it is addressing the diverse needs of enterprises and governments as they adopt blockchain technology. Organizations value the open development and open governance models that we bring to our code projects that are aligned with Linux Foundation open source core principles and our vision is that many critical and important projects will want to be under our umbrella.
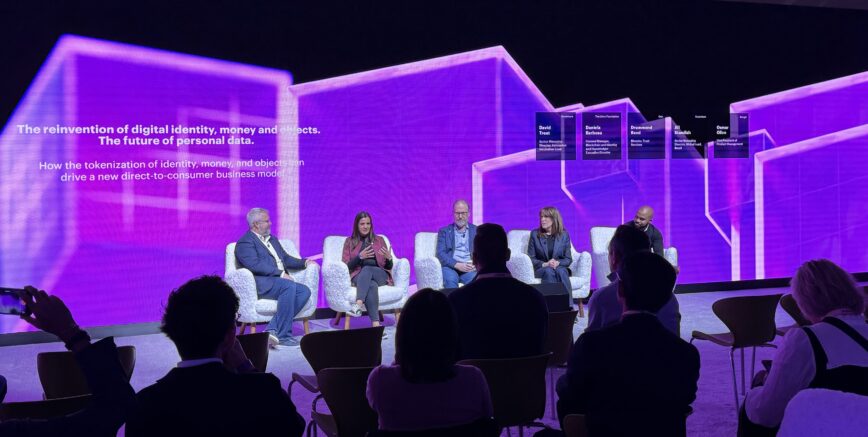

The reinvention of digital identity, money and objects – The future of personal data @ CES 2024
-
How does the Hyperledger project contribute to the broader landscape of blockchain technology?
Answer: Hyperledger Foundation is home to a diverse set of enterprise-grade blockchain technologies, including distributed ledgers, libraries and tools, that are supported by global development communities and deployed in production systems around the world. We also host Hyperledger Labs, our innovation pipeline for new technologies that will keep pushing the market forward on everything from scalability and interoperability to tooling and security.
-
How does open-source culture influence the development and adoption of blockchain technologies in various industries?
Answer: In the blockchain market in particular, open source code is table stakes. The market is built on the idea of transparency. Our community not only embraces an open source mindset but adheres to the rigors of open development, which require a robust community with a diversity of perspectives, well-structured governance, security first mindset and transparent documentation. We hear time and again that the systems built on our technologies are critical infrastructure for financial systems, trade, logistics, transportation, governments and more. Community built software is how you deliver the trust and longevity such systems require.
-
What are some of the most exciting developments or projects currently underway at the Hyperledger Foundation?
Answer: There are important developments underway across our ecosystem ranging from new projects and releases to strategic new members and a growing service provider community. However, what may be the most eye-catching is the accelerating adoption and impact of Hyperledger technologies in a range of new offerings for asset tokenization, including CBDCs, trade finance, climate solutions and digital identity. Hyperledger’s involvement in the Ethereum ecosystem is also exciting. Hyperledger Besu is currently running 5-10% of the Ethereum mainnet as an execution client and is the most adopted EVM (Ethereum Virtual Machine) protocol in use in permissioned financial services use cases.
Engaging with Hyperledger Blockchain for Linux Users
Linux users can contribute significantly to the Hyperledger project, as highlighted in Hyperledger’s blog post. Here are some of the ways you can get started:
- Community Involvement: Join the vibrant Hyperledger community discussions, mailing lists, and social media groups to connect, learn, and share ideas.
- Project Contributions: Offer your skills in coding, documentation, or testing across various Hyperledger projects, especially those that align with your expertise in Linux.
- Events and Meetups: Participate in Hyperledger events, workshops, and meetups to network and stay abreast of the latest developments.
- Educational Resources: Leverage available online resources to enhance your understanding of blockchain in the context of Linux.
- Project Proposals: If you have innovative ideas, consider proposing new projects to the community.
For a comprehensive guide on contributing, visit the Hyperledger Participate page.
Additional reading
Conclusion
In wrapping up our interview with Daniela Barbosa, we’ve traversed the complex landscape where blockchain intertwines with Linux. Her insights shed light on the transformative role of blockchain within the open-source community, highlighting its potential for innovation and security.
May this discussion serve as a catalyst for our continued exploration of these technologies, reminding us of the ever-evolving nature of the digital world and the collaborative spirit that drives it.
Blockchain seems like a good idea on the surface. However, in practice, I haven’t come across situations where it’s the best solution.
I mean, the whole idea of data immutability and a kind of “democracy” for information sounds cool, but the drawbacks are quite significant for real-world use.
The main selling point, that data can’t be altered, isn’t entirely true. Ethereum, for instance, had a fork because a group in charge decided to change some data. In smaller blockchain networks, a malicious actor could set up enough nodes to control over 50%, giving them the power to manipulate things.
Plus, it’s not very eco-friendly. Adding or modifying data involves a lot of computationally intensive processing, often done redundantly by multiple machines simultaneously. So, it ends up consuming a ton of energy just to add a single entry to a database.